What Is Lead?
Lead is a heavy gray metal that was used in many products, including paint before 1978. Many older homes still have lead-based paint on their walls.
You can be exposed to lead by:
- Breathing in or swallowing dust from old paint
- Eating paint chips
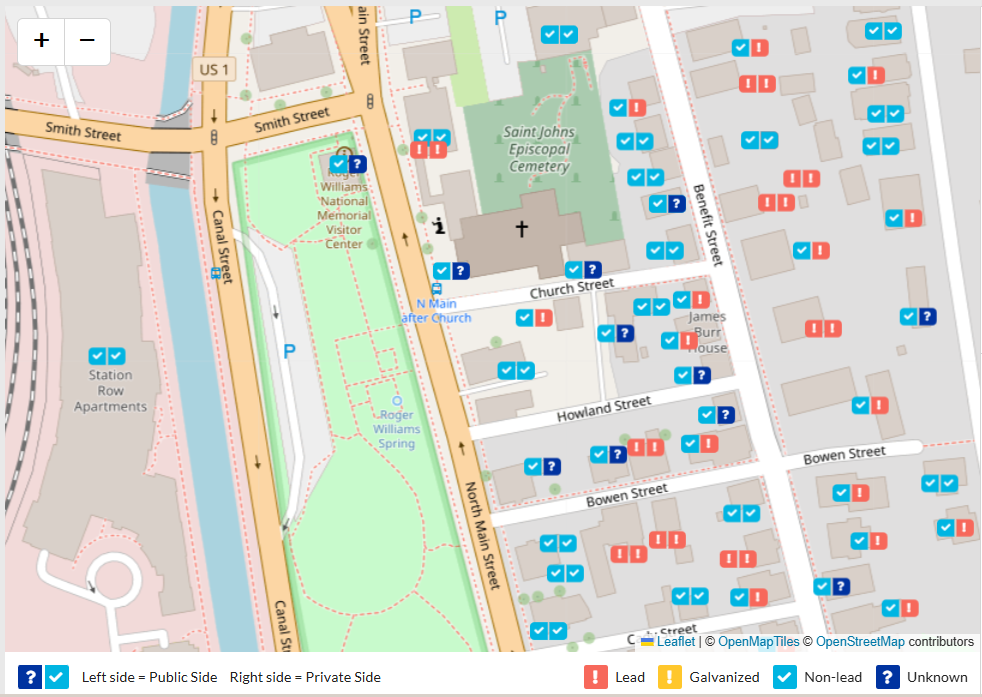
- Drinking water from pipes that have lead
- Eating fruits or vegetables grown in lead-contaminated soil
- Using dishes or cookware made with lead
Lead can be found in many places around the home:
- Peeling or chipping paint
- Dust from lead paint
- Soil and dirt in the yard
- Tap water from old lead pipes
- Dishes made of pottery, ceramic, or crystal
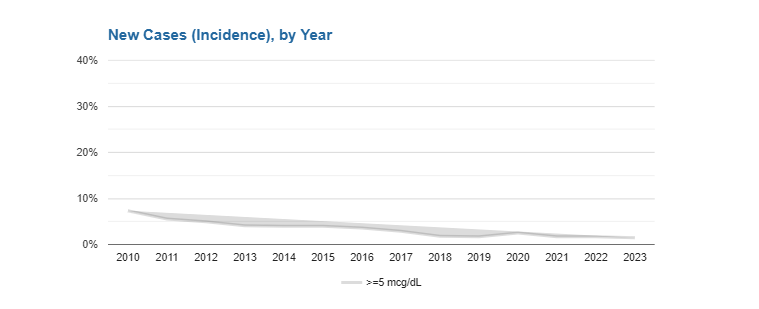
In Rhode Island, the biggest lead danger comes from old paint and paint dust in homes built before 1978.
Who Is Most at Risk?
Anyone can be exposed to lead, but it’s most dangerous for children under 6 years old. Young children often put their hands and toys in their mouths, and these items may have lead dust on them. Even small amounts of lead can cause learning problems, lower IQ, and trouble focusing. The effects can last a lifetime.
Adults are usually exposed to lead at work. Jobs like construction, boat repair, and manufacturing carry higher risks. The state offers free help to businesses to make workplaces safer.
The Good News
Lead exposure is 100% preventable. The Center for Healthy Homes and Environment works across the state to reduce lead exposure and protect families.