Cardiovascular Disease (CVD), including heart disease and stroke, is the leading cause of death and disability in the nation. In the United States, the first leading cause of death is heart disease and the third is stroke. In Rhode Island, heart disease and stroke cause more deaths among men and women than any other disease, in all racial and ethnic groups.
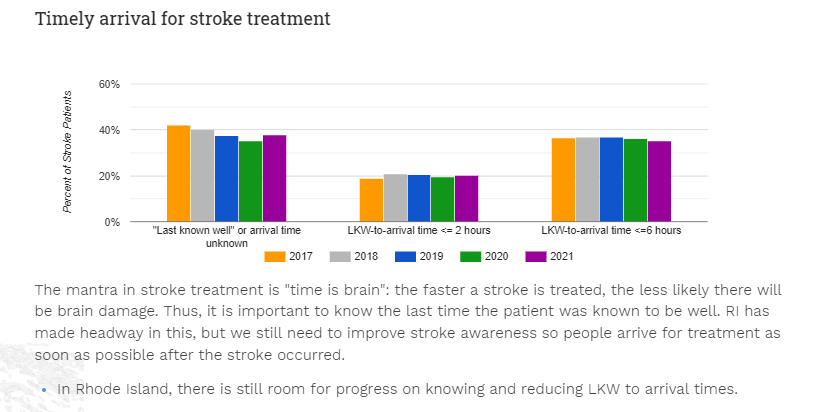
The most common heart disease in the United States is coronary heart disease, which can lead to heart attack. A stroke is sometimes called “a brain attack.” A stroke occurs either when the blood supply to part of the brain is blocked or when a blood vessel in the brain bursts, causing damage to a part of the brain. Knowing the signs and symptoms of heart attack and stroke, calling 911 right away, and getting to a hospital are critical for the best outcomes after having a heart attack or stroke.
Warning Signs
The warning signs of a heart attack include chest discomfort, discomfort in other areas of the upper body, shortness of breath, and other signs such as breaking out in a cold sweat, feeling sick to your stomach, or lightheadedness.
FAST is an acronym used to help people know the warning signs of stroke and what to do if they observe any of these warning signs.
- Face - Ask the person to smile. Does one side of the face droop?
- Arm - Ask the person to raise both arms. Does one arm drift downward?
- Speech - Ask the person to repeat a simple phrase. Is their speech slurred or strange?
- Time - If you observe any of these signs, call 9-1-1 immediately.
What you should do
The best treatment is to lower your risks for heart attack and stroke. This can help to prevent a first attack, reduce the damage after an attack, and prevent an additional future attack. Following these guidelines to lower your risk:
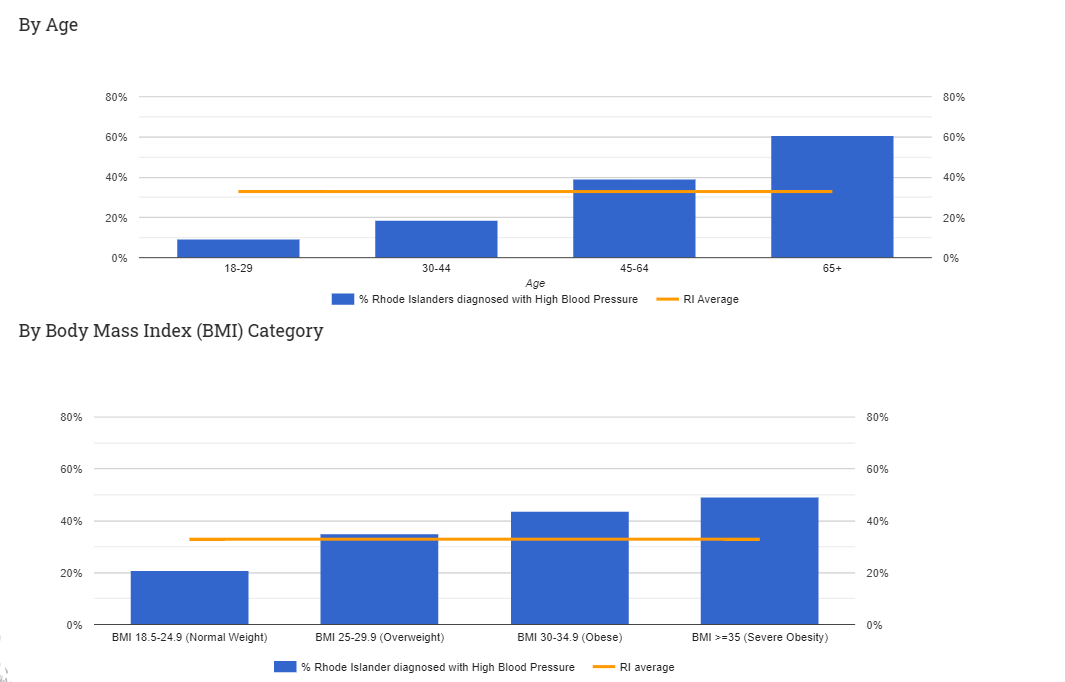
- Keep your blood pressure under control
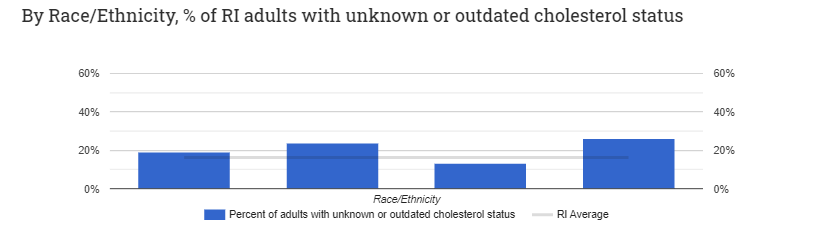
- Reduce high blood cholesterol
- Avoid cigarette smoking
- Maintain a healthy weight
- Reduce salt intake
- Participate in a lifestyle change program