COVID-19 (Coronavirus)
COVID-19 (coronavirus disease 2019) is a disease caused by the Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) virus. This respiratory virus can be very contagious and spread quickly through droplets in the air when an infected person coughs, sneezes, or talks. Anyone infected with COVID-19 can spread it, even if they do not have symptoms. More than 1.2 million people have died of COVID-19 in the United States. Learn more about COVID-19 from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC).
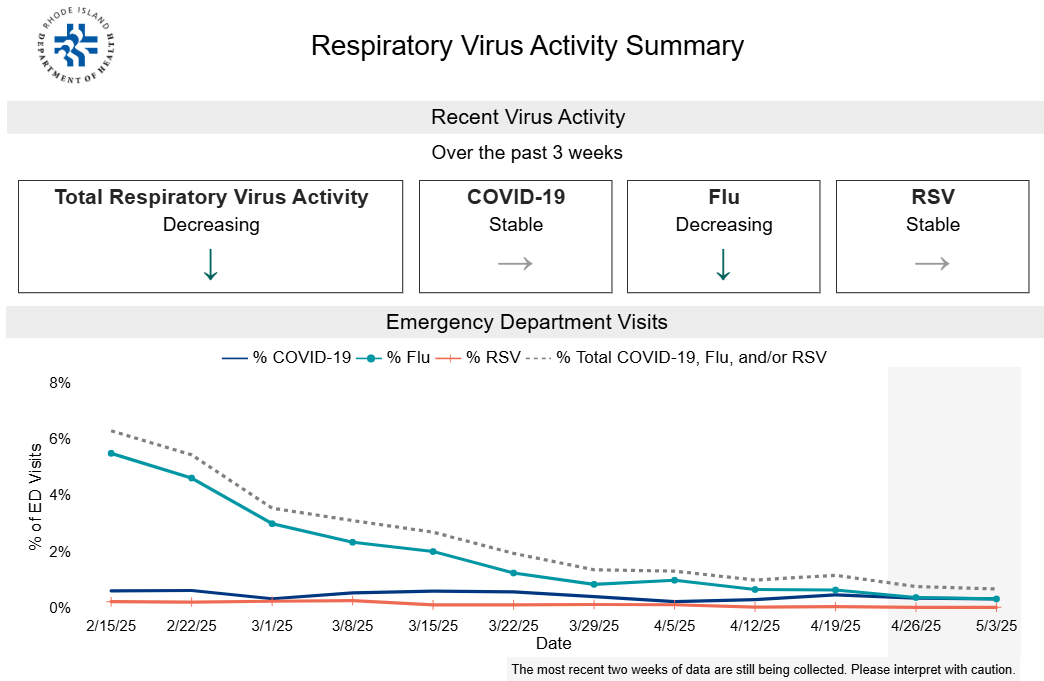
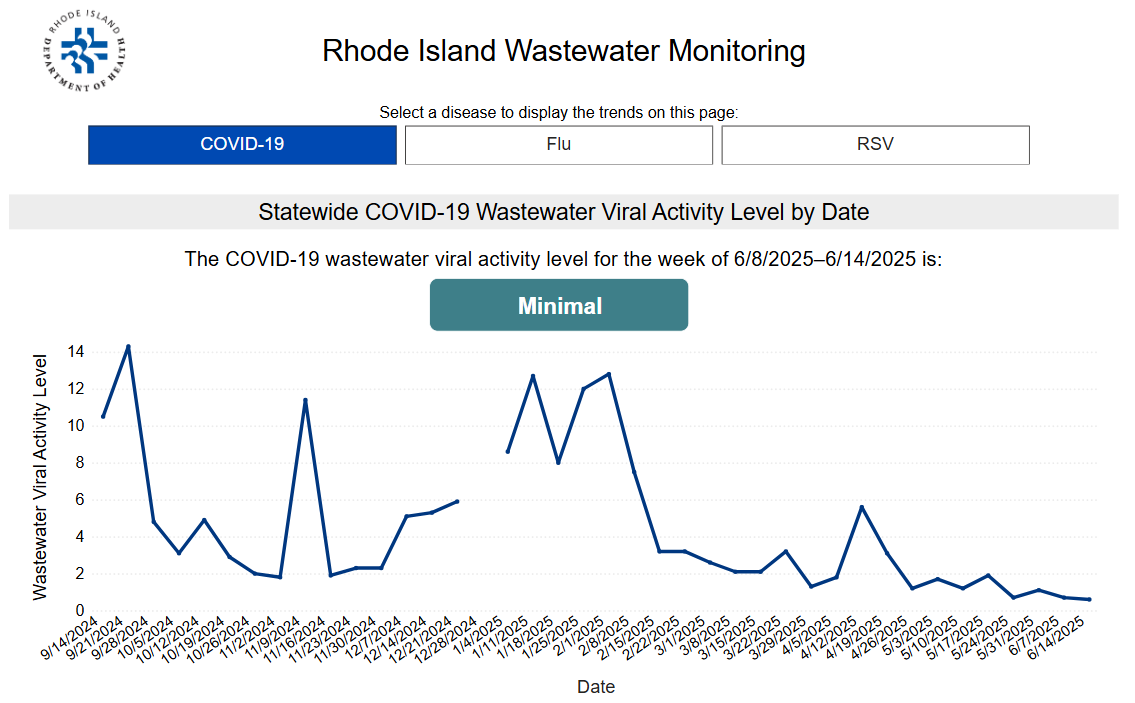
For Rhode Island COVID-19 numbers, visit our Respiratory Virus Data page.
Symptoms
COVID-19 most often attacks your lungs and respiratory system, causing symptoms that can feel like a cold, the flu, or pneumonia. People with COVID-19 have reported a wide range of symptoms ranging from mild symptoms to severe illness. Symptoms may appear 2-14 days after exposure to the virus. People with these symptoms may have COVID-19:
- Cough
- Shortness of breath or difficulty breathing
- Fever or chills
- Muscle or body aches
- Sore throat
- Headache
- Nausea or vomiting
- Diarrhea
- Runny nose or stuffy nose
- Fatigue
- Recent loss of taste or smell
Children have similar symptoms to adults and generally have mild illness. This list does not include all possible symptoms. Other parts of your body may also be affected by the disease.
When to Seek Emergency Medical Attention
If you or anyone you know is having the following symptoms of COVID-19, call 911 or get yourself or that person to the nearest hospital right away. Tell 911 or the hospital you or that person has COVID-19:
- Trouble breathing
- Ongoing pain or pressure in the chest
- New confusion
- Inability to wake or stay awake
- Bluish lips or face
This list does not include all possible symptoms. Call your medical provider for any other symptoms that are severe or concerning to you.
Prevent
The CDC recommends that all people use prevention strategies to protect yourself and others from COVID-19 and other respiratory illnesses.
Vaccinate
To stay protected against COVID-19, it’s important to keep your vaccines up to date. This means getting the latest COVID-19 vaccine when you are eligible. Everyone age 6 months or older can get the COVID-19 vaccine.
Test
If you know when you’re sick with COVID-19, you can get treatment and you can prevent the illness from spreading to others.
Treat
Seek health care right away for testing and/or treatment if you believe you may have a respiratory virus (if you feel sick or tested positive for one) and you have risk factors for severe illness. If you have COVID-19, treatment may be an option to make your symptoms less severe and shorten the time you are sick. You need to start treatment within a few days of when your symptoms begin.
Risk Factors for Severe Illness
Many factors can make it more likely for someone to become very sick from a respiratory virus, including COVID-19. There are several specific considerations for people with certain risk factors for severe illness.
CDC offers separate, specific guidance for healthcare settings, including nursing homes, for COVID-19.
Long COVID
Some people who have been infected with the virus that causes COVID-19 can experience long-term effects from their infection. These effects are known as Long COVID or Post-COVID Conditions.
Resources
Guidance, Recommendations
- What You Need to Know About Fall-Winter Vaccines(Spanish)
- Respiratory Virus Guidance for Congregate Living Settings: Information for Healthcare Workers and Staff Members
- Crisis Standards of Care
- Providing Care and Services for Undocumented Immigrants: Information for Healthcare Workers and Staff Members
- Vaccines for older adults: Stay protected! (English and Spanish)
- Healthcare Worker Return to Work Guidance
- RIDOH Interim Guidance for the 2025-2026 COVID-19 Vaccine
- Vaccines for adults and children with asthma (English and Spanish)
- Adolescent Immunization Schedule: At a Glance (English and Spanish)
Frequently Asked Questions
Guidance, Recommendations, Training
External Resources
Web Pages
Research
Guidance, Recommendations
- COVID-19 Information for Health Care Providers | CDC
- Dental Infection Prevention and Control | CDC
- Infection Control Guidance: SARS-CoV-2 | CDC
- Interim Guidance for Managing Healthcare Personnel with SARS-CoV-2 Infection or Exposure to SARS-CoV-2 | CDC
- Protecting Workers: Guidance on Mitigating and Preventing the Spread of COVID-19 in the Workplace | OSHA
- Safe Practices for Putting On and Taking Off PPE | CDC
- Taking Steps for Cleaner Air for Respiratory Virus Prevention | CDC